Art of bone restoration
 The movements and movements of a person in space – from the simplest to the most complex – are made thanks to the work of the musculoskeletal system, represented by its active part – muscles and passive – bones and their joints. A clear interaction of this duet is possible only under the condition of the anatomical integrity of the structures of both components. Damage to one leads to a partial, and sometimes complete loss of functions of the other. The reasons for which such violations can occur are numerous. These are not only man-made disasters or natural disasters – tsunamis, earthquakes, floods and hurricanes, but also aviation and car accidents, sports or just awkward traffic.
The movements and movements of a person in space – from the simplest to the most complex – are made thanks to the work of the musculoskeletal system, represented by its active part – muscles and passive – bones and their joints. A clear interaction of this duet is possible only under the condition of the anatomical integrity of the structures of both components. Damage to one leads to a partial, and sometimes complete loss of functions of the other. The reasons for which such violations can occur are numerous. These are not only man-made disasters or natural disasters – tsunamis, earthquakes, floods and hurricanes, but also aviation and car accidents, sports or just awkward traffic.
The leading place among injuries, according to the Russian traumatologists, is occupied by road accidents. According to statistics, in our country for 10 thousand cars per year, 12 serious accidents happen. This is the highest level of accidents in the world. Only in 2004, 34 thousand people died on the roads and 250 thousand were injured, a significant proportion of whom belong to mechanical fractures of different severity. Therefore, the problem of improving the methods of rendering first aid, treating and rehabilitating the victims not only does not lose its relevance, but also becomes more acute and urgent.
Implants instead of gypsum
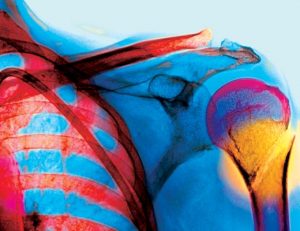
In the total amount of injuries, 80% are fractures of limb bones. Depending on their nature, specialists distinguish over a dozen different types of fractures. However, the choice of treatment method depends not only on the nature of the fracture, but also on a number of other factors: the patient’s general health, physical activity, and type of professional activity. Compared to other types of connective tissue, bone tissue has a unique feature; even serious and extensive defects can be fully repaired in it. The source of the formation of new tissue are stem progenitor cells localized mainly in the bone marrow and hematopoietic organs, and osteogenic cells lining the inner layer of the periosteum, which differentiate at the fracture site and begin to develop, closing the edges of fragments.
The most frequent method of adhesion of the bone is the complete immobilization of the affected limb. After fixation of fragments by imposing external fixing bandages (bandage, plaster, orthopedic – orthoses) or by means of skeletal traction, when a needle is held through the bone, through which the thrust in the form of a certain weight of the counterweight is fixed, the victim for a certain time is literally riveted to a hospital bed. Such strict bed restraint often leads to the occurrence of pressure sores or, even worse, the development of various pathologies of vital systems and organs. But even if it is possible to avoid these complications, prolonged inactivity of the damaged segment leads to muscle atrophy, restriction of movements (contractures) in the joints, which later have to be managed with great difficulty. The modern surgical technologies of osteosynthesis, which are based on the use of special fixative implants for connecting bones, have helped to solve this problem. They sufficiently provide a snug fit and immobility of bone fragments, but at the same time they allow maintaining the motor function of the injured limb.
There are very high demands on the material from which the clips are made. After all, poor-quality metal, which was used at first, often caused metallosis as a result of oxidation when interacting with tissues. Modern implants are made from gentle inert materials that can fully maintain their physicochemical properties during the entire recovery period.
According to the indications, the operation of osteosynthesis is carried out in several ways. With intraosseous sections of different shape, locking rods are inserted through the bone-cerebral canal into the bone, and with locking plates, there are plates with different openings and holes with holes through which screws are screwed into the bone.
For transosseous (extra-focal) osteosynthesis, special devices are used. Our compatriots are most familiar with the apparatus GA. Ilizarov The principle of its “work” is the following: intersecting spokes are fixed in metal rings, which in turn are connected to each other by sliding rods, which make it possible to pull together or push them apart, increasing or weakening the pressure on the bone fragments. By the way, in addition to the treatment of fractures, this apparatus is used to lengthen the limbs. No less popular are the Volkov-Oganesyan hinged-distraction devices, which allow the entire static and dynamic load to be transferred to the design of the device, which creates the possibility of painless movements.